Google Search algorithm ranking factors
Lesson 2 of 6 of our beginner's guide to SEO
How Google ranks your website
So now you understand the purpose of search engines and how people use them, it’s time to get to know the ingredients that make up Google’s much-fabled search algorithm.
To make sure it stays top dog in the search engine world, and to protect its highest-quality results, Google does not publish the specific details of their algorithms.
However, through extensive research and testing, the SEO industry does have a good idea of the factors considered relevant and those that tend to yield the best search engine results rankings.
Over 200 different factors are used to judge the quality of a web page.
Whilst nobody really knows the exact significance and relevance of each of these variables, we do know what some of the key factors are.
Keywords
Keywords are words or phrases that are highly relevant to your web page subject. These words will usually be placed in your page title, and frequently within the text of your web page.
We’ll look into how to identify the right keywords later on in this guide.


On-page SEO
On-page optimisation is the optimisation of a website’s content, text, tags, links, and other elements for the benefit of search engines.
On-page SEO enables high-quality content, but also ensures that the site uses compliant coding and has links and navigation that are easy to follow, pages that load quickly, and accessibility for search engine web crawlers to effectively index your content.
Pound for pound, on-page optimisation is probably the single most important factor when it comes to identifying a sites content and ranking it accordingly – which is why we cover it in-depth in the next lesson.
Inbound links
In addition to on-page optimisation, a web page will benefit from a strong backlink profile.
Your link profile is the collection of external links (from other websites) that point to your own website/pages.
Google considers the number of links that point to a particular page as well as the authority of the pages that provide those links and their relevance.
Linking is one area of SEO that has evolved a lot over time. Reciprocal links and links from link farms (pages that have been set up to link to one another, providing little to no content) will not benefit your website long-term, and can eventually harm its reputation.
Worse still, these types of links could land you with a Google penalty if your site has an unnatural link profile.
The best kind of links come from high authority websites that have chosen to link to your page because your high quality, relevant content – these types of links can be hard to come by however.
If you provide regular, significant quality content, links will eventually come naturally over time.

Social signals
Because social media sites such as Facebook, Twitter and Google+ function as enormous hives of human interaction, debate and opinion, it is only natural that search engines try to harness the data these platforms provide.
Afterall, web page that gets tweeted, liked, shared or commented upon must be offering some value, right?
A number of different social signals, such as comments, shares, and likes, are all deemed to be indicators of the quality of a particular web page.
- Number of likes of your Facebook page
- Number of shares, likes or comments on a link posted to Facebook
- Number of followers on your Twitter profile
- Number of tweets mentioning your brand name or company URL
- Number of people who have you in their Google+ circles
- Number of Google +1s that a web page has
Of course, using social media provides other fantastic benefits for your business, especially in terms of brand exposure and customer service.
Grow your social media presence with our guides to Facebook and Twitter.
Page Speed
In 2010, Google announced that page speed was being introduced as a ranking factor in their algorithms.
Whilst fast-loading pages do not strictly receive better rankings, slow-loading pages can be penalised and pushed further down in the rankings.
This means that optimising your web pages to load quickly, and ensuring that all elements on a page load efficiently, can help your SEO efforts and prevent users from leaving your web page in frustration.
Use a tool like Google's free PageSpeed Insights to measure how long your page takes to load.
This will give your page a score out of 100 for desktop loading, as well as a separate score for the speed at which your page loads on mobile devices.
It also gives advice regarding potential improvements such as optimising images and benefiting from browser caching to yield the best load times.
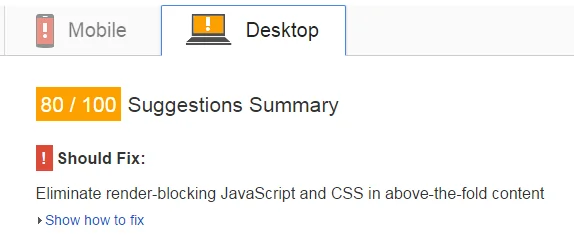
When using a tool like PageSpeed Insights, you will typically find that your site loads more quickly on a desktop computer than it does on a mobile device.
It's important to consider that more and more people now use their phone or tablet when going online.
Make sure your site loads quickly on both types of device – otherwise you could be alienating a large segment of your potential visitors.
Mobile optimisation
Over half of all Google searches are now made on mobile and tablet devices. This is a big deal.
In a bid to help improve user-experience for mobile searches, Google made an announcement in 2015 Google announced that “mobile friendliness” would become a ranking factor.
This change to the ranking algorithm meant that Google are now looking to prioritise mobile friendly sites when people search on mobile devices – makes total sense right?
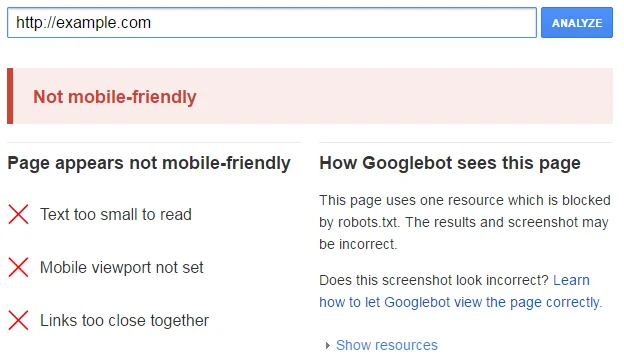
If your site is not mobile optimised you may be missing out. To find out how Google view your site you can use their mobile-friendly testing tool.
There are a few different types of mobile friendly sites available:
- Responsive design: This method sends the same HTML code to any device that requests it (desktop, mobile, tablet) and the code resizes the imagery and text on the page accordingly to fit the page/screen resolution.
- Mobile app: A separate app installed on a mobile or tablet advice which would serve a mobile version of a website – different to the usual desktop version.
- Separate mobile site: A browser based method that uses different HTML code to the regular desktop site, and would send users to a separate mobile address. For example, your regular site would be http://www.example.com, whilst your mobile site might be http://mobile.example.com – this is effectively two different websites.
Google recommends using responsive design – since the other types of mobile site delivery can cause problem with duplicate content and inconsistent user experience.
Responsive designs are fairly commonplace today, but older websites might not be optimised.
Take a look at Google’s guide to getting started with mobile design. If you have little or no experience with HTML code and designing websites, you may want to consider hiring a web designer when making your site mobile-friendly.
SSL (HTTP secure)
Back in 2014 Google also confirmed that HTTPS was now considered in their ranking algorithm, with Google looking to help make the web a more secure place by offering benefits for webmasters who secure their websites using an SSL certificate.
SSL certification is the industry-standard method of encrypting data sent between a website and the end user.
You can easily tell if the site you’re on is using SSL, by looking for the “https” in your web browser address bar, where you’ll usually see a green padlock.
It’s important to note that in Google’s original announcement they indicated they may strengthen this ranking signal in the future.
How much of a ranking boost gives using an SSL certificate gives your site is up for debate, but it’s certainly a ranking factor (where it wasn’t before).
Check out our guide on the SEO benefits for SSL for more information.
Algorithm changes
Google’s algorithms have undergone major changes in recent years, and what was once considered essential to an SEO campaign may be ineffective now.
Reciprocal linking and keyword stuffing were popular because they were effective. Nowadays, they are of little value to a modern SEO campaign, and could even result in a web page being penalised instead.
It is important to stay on top of the latest changes in order to determine what currently works and what doesn’t.
Google is constantly moving the goal posts. Social ranking factors, SSL (https) and site speed wouldn’t have featured in this list a few of years ago, but now they’re vital.
Only through regular research and study can you stay up-to-the-minute with the latest goings-on in the Google algorithm department.
Check out our blog post for more details on how algorithm changes can affect your website.